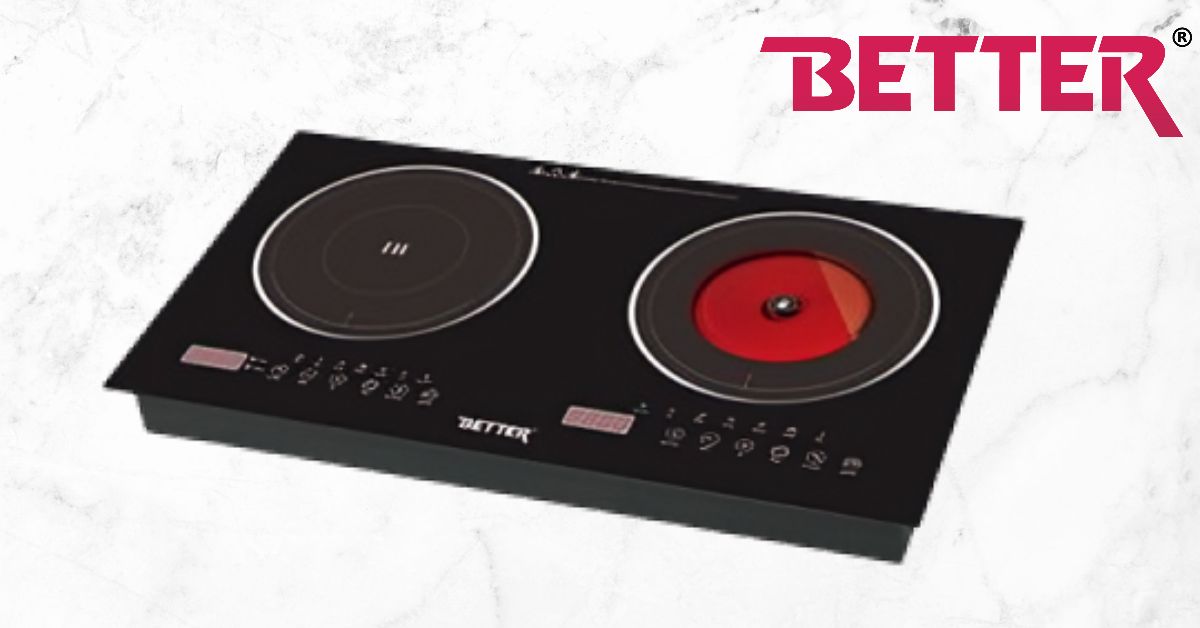
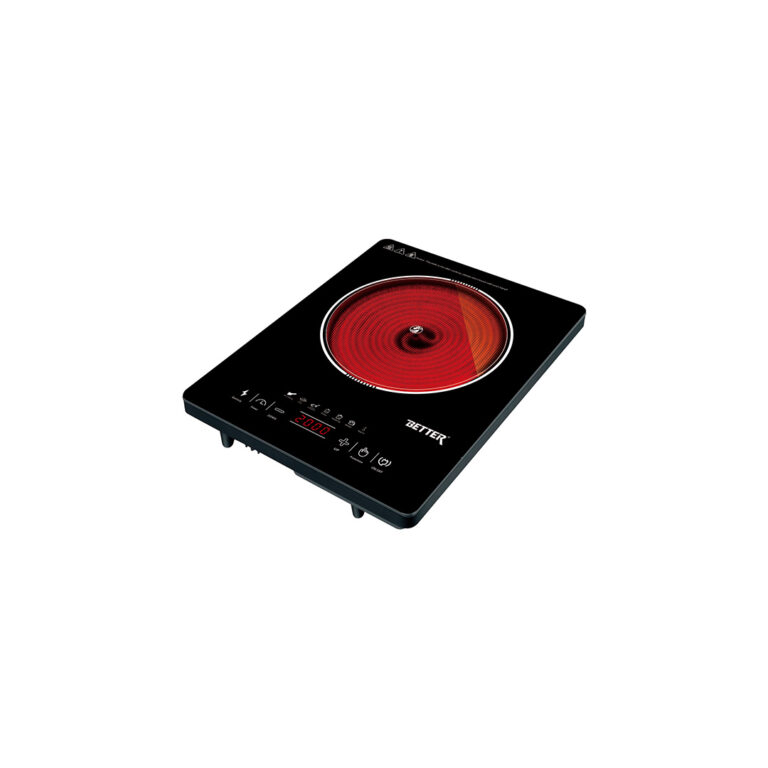
How Does an Induction Oven Work? The Magic Behind It
July 28, 2024
Share To:
Induction oven has been gaining popularity over the years because they efficiently and precisely cook food. But many are curious about how does an induction oven work.
An induction oven heats food due to the production of an electromagnetic field. When it is ignited, an electric current passes through a metal coil, thereby producing a magnetic field.
Afterward, this magnetic field penetrates the metal of the cooking pan and induces a current in the pan. Then, the current dissipates energy in the form of heat and cooks the food in the pan.
In this blog, we will discuss in detail the science behind induction cooking and its major components, outline one process, benefits, and probable drawbacks, and compare it with other oven types.
Table of contents
What is Induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a changing magnetic field. As you will see, electricity and magnetism are not independent entities; they are two variables from a single phenomenon, electromagnetism.
It is because of this that a change in a magnetic field results in the generation of electric current, and vice versa. Also, a change in the electric field across a conductor produces a magnetic field.
The latter underlies the workings of induction cooktops, which is pretty much all you need to know to understand how induction cooktops work.
Understanding the Basics of Induction Cooking
An induction oven, popularly known as an induction cooktop or stove, is an appliance designed to directly heat cookware with the help of electromagnetic induction. Here is how this works:
How does an Induction Oven Work? The Science Behind Induction Cooking
To understand how induction ovens work, one must first know the science behind induction cooking.
Unlike a traditional gas or electric oven, heat is directly produced in cookware with the help of electromagnetic fields. This skips all the intermediate steps involved in conventional heating and results in faster and more efficient cooking.
Similarly, induction cooking uses extremely accurate electromagnetic fields that allow for temperature and cooking time control.
These could be beneficial in preparing some of the finer dishes that require specific amounts of heat to achieve a perfect result. It is in this instant heat variability that induction cooking allows chefs to have more flexibility and control over their dishes.
Key Components of an Induction Oven
An induction oven comprises some major components. The first essential component is a copper coil under the cooking surface.
When an electric current flows through this coil, it generates an alternating magnetic field. This magnetic field then interacts with the ferromagnetic material present in compatible cookware, inducing an electrical current within it.
Another important element is the control panel, where users can change the cooking settings and temperature.
There are also sensors in induction ovens that monitor the temperature of cookware and change the magnetic field accordingly to avoid overheating and produce accurate results.
Many induction ovens also come with features such as automatic pan detection. It detects compatible cookware placed on the cooking surface, only turning on the heating if there is a pot or pan on top of it.
Therefore, this enhances safety since it reduces the risk of accidental burns and saves energy since there will be less heat loss.
Step-by-Step Guide to How Induction Ovens Heat Food
Let us go through the step-by-step procedure for how induction ovens heat food:
- When powered on, an electric current flows through the copper coil beneath the surface of the cooktop.
- This electric current will create a very high-frequency, alternating magnetic field.
- Placing compatible cookware on the cooktop will induce an electrical current within the cookware from the magnetic field.
- The induced electrical current causes resistive heating of the cookware and increases its temperature quickly.
- Again, this raises the temperature of food uniformly since it transfers the heat from the cookware to the food.
Advantages of Induction Cooking

1. Efficiency and Speed of Induction Ovens
Induction cooking is very effective because the heating occurs directly in the cookware while very little heat gets wasted or lost.
The total efficiency generally stands around 90%, and that of the traditional models of electric or gas stoves is normally within the range of 70–75%.
This is because the heat is directed directly at the utensil, making the food much hotter than with traditional cooking.
2. Safety Features in Induction Cooking
The cooktop remains relatively cool because the heating occurs directly in the cookware, while very little heat gets wasted or lost.
The total efficiency generally stands around 90%, and that of the traditional models of electric or gas stoves is normally within the range of 70–75%.
This is because the heat is directed directly at the utensil, making the food much hotter than with traditional cooking and cookware. This, in turn, reduces the risk of burns.
Similarly, almost all induction cooktops come equipped with a variety of safety measures, like switching off automatically in the event of failure to detect any cookware.
Another important safety advantage associated with induction cooking is the cool cooktop surface. In comparison with gas or radiant electric cooktops, which may retain some heat and hence pose a burn hazard even after switching off, an induction cooktop surface remains relatively cool to the touch.
This feature not only minimizes the chances of burning during cooking but also makes cleaning up the splatters and spills spilled on the surface very easy. It is because it cools down very fast, and the area can just be wiped clean.
3. Less Pollution
Much cooking around the world uses combustion-type cooking, including natural gas flames or open fires in developing countries. Many people might be surprised to learn just how much nitrogen oxide gas stoves release, typically associated with diesel engines and outdoor smog.
Electric cooking, although it can still give off “particulates” of air pollution, particularly when you’re doing things like frying, generally is cleaner and healthier to have around.
Potential Drawbacks of Induction Ovens
i. Cookware Requirements for Induction Cooking
One possible drawback to induction cooking is that the cookware must be compatible. Induction ovens will only work with cookware made from magnetic materials, like cast iron or stainless steel.
Items made of aluminum or copper won’t work on an induction cooktop; they simply won’t heat up. Upgrading your cookware collection for induction is an additional investment.
While the initial investment in induction-compatible cookware may be higher, the long-term benefits of these pots and pans will outweigh this cost.
This cookware heats faster and more evenly than traditional options, enabling quicker cooking and potential energy savings.
ii. Cost and Maintenance Considerations
While induction ovens offer several advantages, they typically cost more than conventional gas or electric ovens due to the advanced technology and materials used in their construction.
Users also find that induction cooktops demand more maintenance, such as regular cleaning to remove residue and maintain optimal performance.
Similarly, induction ovens require a larger initial investment. Many users find that energy efficiency and precise cooking capabilities lead to long-term savings on utility bills.
Because of the precise heat control and rapid response to temperature changes minimize energy waste during cooking. Also, maintenance and repair costs for induction ovens should be considered in overall ownership costs.
Comparing Induction Ovens to Other Types
A. Induction vs Gas Ovens
Comparing induction and gas ovens requires careful consideration. While gas ovens offer precise flame control, induction ovens provide even finer heat control through responsiveness and adjustability.
Many people seeking energy-efficient appliances favor induction ovens due to their rapid heating and cooling times, giving them another advantage over other ovens.
Professional chefs preferred gas ovens for many years because of their ability to easily adjust heat levels, accommodating a wide range of cooking techniques.
But in recent years, induction ovens have gained popularity due to their ability to instantly adjust and precisely control temperature, a crucial feature for delicate cooking tasks.
B. Induction vs. Electric Ovens
Electric ovens, much like induction ovens, are sources of constant heat with precision in temperature control.
However, induction ovens generally have quicker heat-ups and more effective cooking methods since the heating process occurs directly in the pot. Electric ovens may take their time to preheat and, at times, cook food unevenly.
Another major advantage of electric ovens is that they are already widely available in the market and are more affordable than their induction oven counterparts.
Households commonly use electric ovens due to their user-friendly operation and lower initial cost. Still, induction ovens are gaining popularity due to their energy efficiency and faster cooking times, making them an attractive option for those seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills.
Why should you buy an induction Oven from Better?
Are you looking to upgrade your kitchen with electric appliances? If yes, you’ve come to the right place.
There are many reasons to choose an induction oven from TheBetterAppliances. Since, induction ovens offer fast cooking with less energy consumption, helping you save significantly on electricity bills.
The cooktop remains cool, enhancing safety and making it easy to clean as spills don’t burn onto the surface. The induction oven offers perfect temperature control for perfect cooking.
They come with modern designs that not only add style to your kitchen but are also relatively more eco-friendly by consuming less energy. In a nutshell, an induction oven cooks fast, safely, and efficiently.
Conclusion
Induction ovens make use of electromagnetic fields that induce electrical currents in compatible cookware to provide efficient and very precise heating.
They might require some specific needs and maintenance, but they have numerous benefits to offer, such as efficiency, speed, and improved safety features that make them quite desirable for the kitchens of today.
Compared with most other oven types, their superior performance and energy efficiency have made induction ovens a preferred choice for many cooking enthusiasts.
Therefore, any questions about how does an induction oven work has now been answered.
FAQ
A: An induction oven generates a magnetic field with the help of a coil directly under the cooktop. Placing suitable cookware on this magnetic field induces an electric current on it, thus heating it and therefore cooking the food.
A: Cookware should always be ferromagnetic. This includes cookware made from cast iron, some stainless steel, and other magnetic materials. Moreover, cookware should have a bottom that is flat to work efficiently.
A: Induction cooking is more efficient because it directly heats only cookware and not the cooktop or air around it, thus wasting less energy.
A: Induction ovens are very safe. The cooktop remains relatively cool since it is the cookware that generates the heat. Most induction cooktops also include safety features like automatic shut-off if no cookware is detected.
A: Yes, induction cooking normally is quicker because the heat comes right there in the cookware, making it hotter and more efficient.
Related Blogs


Best Electric Geyser in Nepal (Newly Updated) | Top 7 Picks